Just like the roads and railways that provide transportation across the country, the cyber arena relies on its own transportation systems to navigate data flows. However, data traveling through cyberspace is subject to various risks, which leads to the need for protective measures such as a “tunnel.” In this article, we’ll take a look at the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) and compare it to other VPN protocols.
What is the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)?
L2TP serves as a secure and efficient means of transferring data over public networks, in particular, within virtual private networks (VPNs). Originating in 2000 through the joint efforts of Microsoft and Cisco engineers, L2TP appeared as a modernized alternative to the outdated Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), designated by RFC 2661. By combining components of PPTP and Cisco’s Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (LTF), L2TP establishes reliable point-to-point connections at OSI Layer 2. Subsequently, in 2005, the protocol underwent a significant upgrade with the release of L2TPv3, improving encapsulation features and overall speed. Today, L2TP is a core protocol in VPN networks, often used in conjunction with the IPSec security and authentication protocol. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at L2TP, exploring its functionality, applications, and performance characteristics in various scenarios.
How does L2TP work?
The online world has its own traffic system, where your data can encounter various dangers while being in transit. That is why using VPN protocols will protect you due to tunneling that adds a layer of protection. Here is a detailed overview of how the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (or L2TP) works:
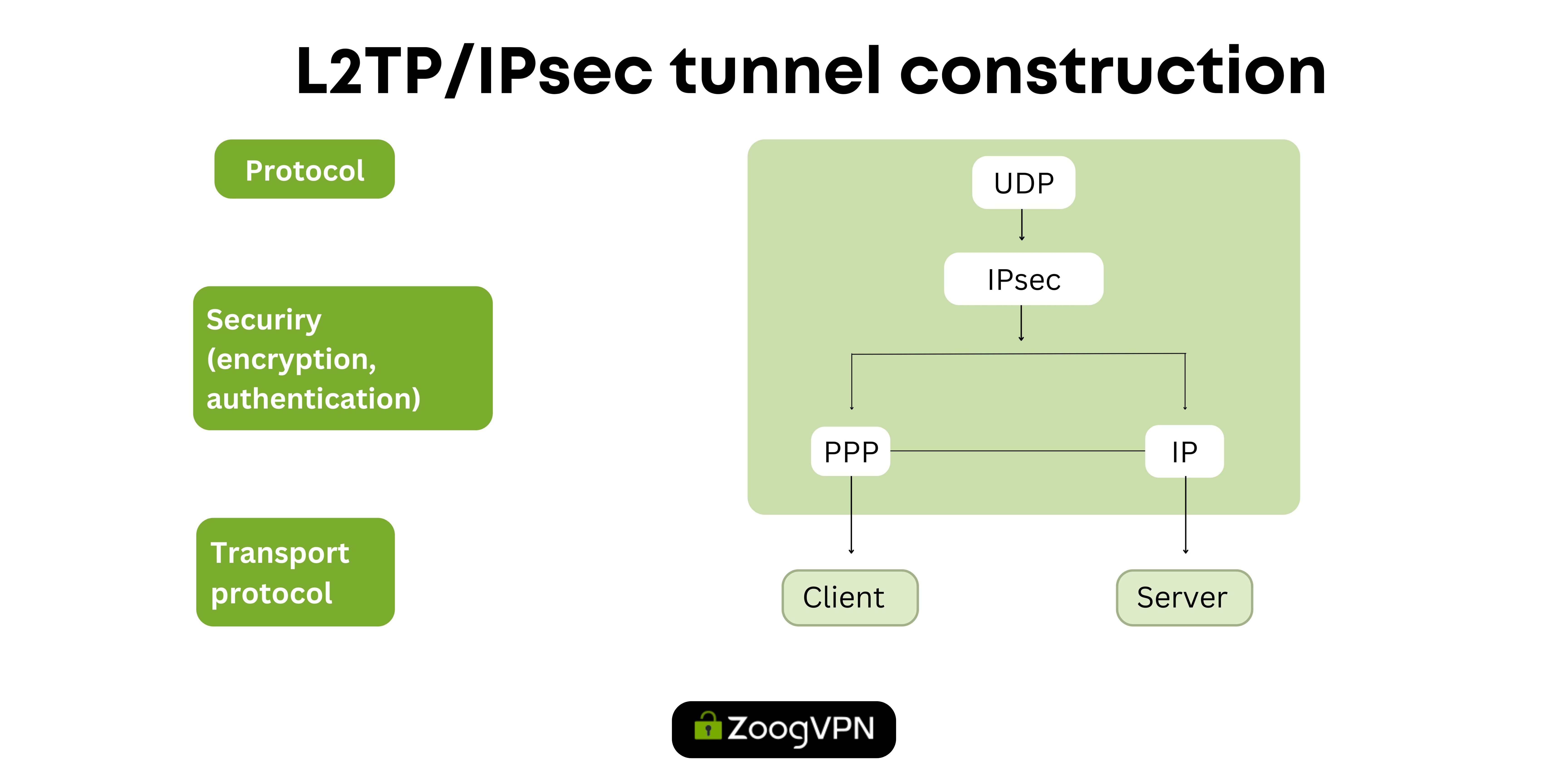
L2TP operates by transporting OSI Layer 2 traffic across Layer 3 networks through a three-stage process.
- First, a connection is established between the LAC and the LNS, which serve as the endpoints of the tunnel. This involves negotiating and assigning IP addresses to each network device.
- Next, L2TP negotiates the transmission by activating the PPP link layer and encapsulating the data frames for transmission.
- A tunnel is then created that connects the remote workstation to the LAC at the provider. The LAC accepts the tunnel, assigns a network slot, and the LNS generates a virtual PPP interface for data exchange.
- Upon receipt, the LNS removes encapsulation information, passing individual IP packets to the local network server as regular frames. This process enables Layer 2 network identities to communicate across vast distances, facilitating secure transmission of confidential data and workflows between remote workstations and central servers.
This procedure involves breaking up data into packets, encrypting them with IPsec for security, encapsulating them into L2TP packets to create a secure tunnel over the public network, transmitting them, unpacking and decrypting at the receiving end, thereby restoring the original data accessible on the local area network (LAN) connected to the VPN server.
How IPSec works with L2TP?
L2TP does not work in lock-step. While the protocol itself lacks encryption and authentication capabilities, it is supplemented by additional security measures provided by other protocols. Typically, the Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) protocol is used to perform these vital functions, resulting in the widely recognized L2TP/IPSec combination.
With the introduction of IPSec, L2TP becomes a robust VPN solution that provides end-to-end security. Thanks to sophisticated encryption methods such as 256-bit AES encryption and Internet Key Exchange (IKE), both protocols work in tandem to protect data. Using the UDP 500 port, data is encapsulated in Encapsulated Security Payloads (ESP), which ensures secure transmission.
ESP plays a key role by allowing the LAC and LNS to authenticate and decrypt the data payload, ensuring secure and authenticated transmission. This encryption not only protects multi-protocol packets and IP headers but also masks the actual data, allowing smooth routing across virtual networks. L2TP serves as a communication channel, making it easy to set up connections to securely transmit this encrypted data.
What L2TP is regularly used for?
Originally developed to replace expensive dial-up connections for remote networks, L2TP simplifies communication between different branches of an organization. By using Layer 2 tunneling, it simplifies Internet communications, reducing costs and increasing security. Since its invention in 2000, L2TP has become a key foundation in a variety of business applications, demonstrating its versatility in numerous scenarios:
1. L2TP as a VPN: L2TP by itself cannot function as a VPN protocol; it needs to be paired with another protocol, typically IPSec, to provide end-to-end security and anonymity. This combination facilitates secure connections between remote devices and central offices. L2TP creates direct tunnels for Layer 2 traffic, while IPSec adds layers of encryption and authentication to ensure data confidentiality. Wide compatibility with operating systems including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android makes it available to a variety of device ecosystems.
2. L2TP for extending the local network: Companies use L2TP to extend LAN-based corporate networks to include remote devices, making it easier to set up remote work. Stable tunnels are created between the remote devices and the central LAN, providing seamless connectivity between different locations or departments.
3. L2TP in ISP networks: ISPs use L2TP tunnels to manage traffic routing and resell network bandwidth to private customers. This allows ISPs to securely route traffic without compromising customer privacy, as IPSec encryption protects communications between different local networks.
4. L2TP in public Wi-Fi networks: Large organizations such as educational institutions and airports use L2TP tunneling to build and secure public Wi-Fi networks. By maintaining a network of access points, organizations create secure L2TP sessions, reducing the cost and complexity of providing Internet access in different locations.
Essentially, L2TP’s flexibility and robust security features make it the best choice for a variety of network use cases, offering cost-effective solutions while ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
L2TP features
L2TP, despite being an old data tunneling protocol, is still widely used due to its features. Here are some of them that have contributed to the continued popularity of L2TP:
| Compatibility | L2TP, when combined with IPsec, offers wide support across a variety of devices and operating systems, including Windows, MacOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and routers. |
| Multiprotocol Support | Designed to interoperate with a variety of protocols that secure tunnel data, L2TP can support a variety of higher-level protocols, including IPV4 and IPv6. |
| Integration with PPP | By using Point-to-Point (PPP) to encapsulate data in the tunnel, L2TP extends its functionality to include features such as authentication, encryption (in combination with IPsec), and compression. However, newer VPN protocols have advanced to use more robust and adaptive encapsulation and encryption techniques. |
| Voluntary and Forced Tunneling | L2TP supports both voluntary tunneling initiated by the VPN user and forced tunneling initiated by the network operator. This flexibility is tailored to different network configurations and user preferences. |
Advantages of L2TP
Increased security with IPSec: When Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol is paired with IPSec, data is highly protected and confidential. IPSec provides strong encryption that makes data virtually impenetrable. Although there are rumors of a breach by the NSA, there is no concrete evidence to prove that the protocol has been compromised.
Easy setup: Setting up an L2TP VPN connection is very easy. The protocol is integrated into major operating systems, making it easy to set up quickly. For example, users can set up an L2TP VPN effortlessly using network settings in Microsoft Windows.
Flexible network: A Layer 2 connection has clear advantages over a Layer 3 VPN. Companies benefit from easier infrastructure sharing across multiple locations and seamless movement of virtual machine infrastructure between devices. Unlike PPTP, which is limited to IP tunnels, L2TP supports a variety of tunnel environments.
Speed: L2TP is known for its fast performance. Often, its speed matches that of unencrypted connections, ensuring efficient data transfer.
Disadvantages of L2TP
Firewall Challenges: Operating on port 500, L2TP may encounter firewall and NAT gateway hurdles. Typically, L2TP passthrough is necessary for seamless protocol transmission across firewalls.
Speed Reduction with IPSec: The speed benefits of raw L2TP may diminish under IPSec encryption. This effect is particularly pronounced with double encapsulation on VPN connections.
Instability: Firewall and connectivity issues can make L2TP/IPSec less reliable compared to alternative VPN protocols like WireGuard or OpenVPN.
FAQ
1. Is L2TP VPN safe?
L2TP is a VPN protocol designed as a secure replacement for PPTP. Using the AES algorithm, encrypts data with a strong 256-bit key. When integrated into VPN settings, L2TP/IPsec has no significant vulnerabilities that could potentially expose personal information.
2. What are the differences between L2TP/IPSec and other VPN protocols in terms of cybersecurity?
L2TP/IPSec stands out as the top-level VPN protocol for cybersecurity. Its strong encryption algorithms protect the data being transmitted, preventing hackers from attempting to intercept and decrypt it. This protocol offers a higher level of security than others, making it the best option for cybersecurity. Furthermore, its frequent updates and improvements strengthen its reputation as a powerful VPN protocol.



























