The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, commonly known as PPTP was Initially developed by Microsoft in 1999. PPTP gained popularity as a simple solution for encrypting communications and creating secure encrypted tunnels in the early 2000s. However, with age, it has developed some drawbacks, especially in terms of security. In this guide, we will take a close look at what is PPTP, and what are benefits and drawbacks it suggests to the users.
What is PPTP?
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is the primary method for creating virtual private networks (VPNs), offering remotely located users a secure way to connect to private servers and transfer data over unreliable networks such as the Internet.
Although PPTP is an outdated VPN protocol, it still attracts users for its simplicity and speed, despite the appearance of more advanced alternatives such as WireGuard, L2TP/IPsec, IKEv2/IPsec, and OpenVPN, primarily due to its ease of setup. Even though PPTP encrypts data for transmission, its encryption methods have become outdated over time, leaving user information exposed to potential hacks. Despite these limitations, PPTP maintains a niche that is preferred by some advanced users in certain situations due to its historical role in VPN implementation.
How PPTP works
PPTP, or Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, works by creating a secure tunnel between two points on a network by encapsulating PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) packets as they are transmitted over the Internet. This encapsulation process creates a protective layer around the transmitted data, allowing it to be repackaged and sent securely over the Internet. However, tunneling alone is not enough to protect data, so you need to use a VPN (virtual private network) to encrypt the information being transmitted.
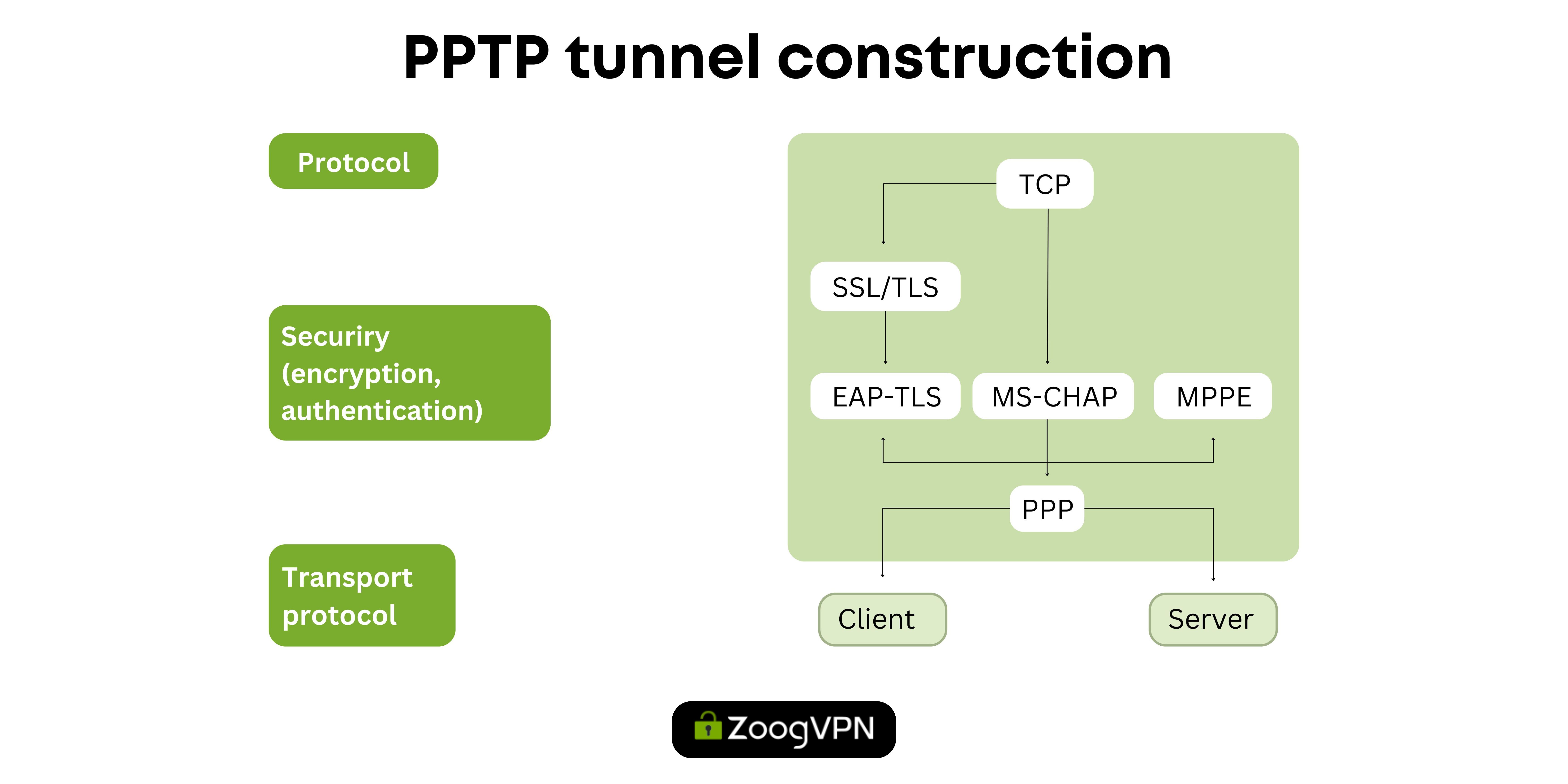
Once a PPTP connection is established between the client and the server, the protocol simplifies the transmission of control messages and data packets. Control messages are responsible for managing the VPN connection, including initiating and terminating it when necessary, while data packets contain the information exchanged over the tunnel. These packets cover all the sites visited and the actions performed on them, ensuring a complete data transfer.
Although PPTP performs the basic operations typical of most VPN protocols, including authentication, tunneling, data encryption/encapsulation, and transportation, its security measures have come under intense attack due to outdated authentication and encryption methods. Despite their simplicity and widespread use, PPTP VPNs are vulnerable to security flaws, making them less reliable for maintaining secure Internet connections.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the PPTP?
The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is one of the oldest and most widely used VPN protocols, known for its simplicity and speed. While it offers a quick and easy setup, it also has some security issues. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of PPTP to understand its importance in VPN usage.
Pros of Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
PPTP is a quick and easy VPN solution that is ideal for those who prefer speed and flexibility. Below are the main pros of using PPTP VPN.
| Advantages | Description |
| Easy to set up | PPTP is known for its simplicity, making it accessible even to users with limited technical knowledge. |
| Fast | PPTP offers fast data transfer due to its low level of encryption, resulting in minimal network processing cost. |
| Wide compatibility | PPTP is compatible with various operating systems, ensuring broad accessibility across different platforms. |
Cons of Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
Although PPTP is easy to set up and provides high speeds, it lacks a critical aspect: VPN security. Let’s take a look at its main cons.
| Disadvantages | |
| Insecure encryption algorithms | PPTP relies on outdated encryption algorithms, such as Microsoft’s MPPE, which are susceptible to attacks. |
| Poor authentication methods | The authentication protocol used by PPTP, MS-CHAP, has numerous weaknesses and vulnerabilities. |
| Vulnerable to brute-force attacks | PPTP’s short encryption keys make it susceptible to brute-force attacks, compromising user data security. |
| Susceptible to firewall blocking | PPTP’s lack of standardized VPN port numbers makes it easy for firewalls to block, leading to connectivity issues. |
| Lack of standardized VPN port numbers | The absence of standardized port numbers makes PPTP more vulnerable to detection and blocking by firewalls. |
While PPTP offers simplicity and speed, its security vulnerabilities cannot be ignored. Users should weigh the convenience of easy setup against the risks associated with insufficient encryption and authentication. With more secure VPN protocols available, such as WireGuard and OpenVPN, it’s important to consider all the compromises before choosing PPTP for your VPN implementation.
What is PPTP Passthrough?
PPTP Passthrough is an important router feature aimed at overcoming connectivity issues between PPTP VPN connections and routers that use NAT (Network Address Translation). NAT, which is commonly used by routers, converts private IP addresses into a single public IP address to increase privacy. However, this setup creates obstacles for older VPN protocols, such as PPTP, which are not compatible with NAT and may encounter connection problems.
To address this limitation, PPTP Passthrough adds a unique caller ID to PPTP traffic, effectively replacing NAT. This unique identifier allows PPTP traffic that would normally use NAT-incompatible VPN ports to pass through routers and firewalls without interruption. This way, PPTP connections can reach the VPN server without being blocked or compromised by NAT restrictions.
While PPTP Passthrough is essential for routers that support older protocols such as PPTP, it is not required for modern and more secure VPN protocols such as OpenVPN, IKEv2, and WireGuard. These modern protocols are inherently NAT-enabled and do not require Passthrough to establish a connection.
Is PPTP secure to use?
When considering PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) security, it’s important to recognize its significant shortcomings. PPTP has long been known for its weaknesses and lack of strong encryption, making it an insecure choice for VPN connections. The protocol uses outdated encryption algorithms, such as Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE), which are known to be exposed to various security threats.
PPTP’s weak encryption makes it particularly susceptible to attacks such as brute force attacks and unauthorized access. Its encryption methods have become outdated over time, leaving users at risk for things like data theft and communication manipulation. The lack of strong mutual authentication further aggravates the protocol’s security issues, making it vulnerable to cybercriminals.
In summary, PPTP’s security flaws make it unsuitable for ensuring the privacy and security of VPN connections in today’s threat landscape. While it may offer ease of setup and fast performance, these benefits are outweighed by the significant risks associated with its insufficient security measures. Therefore, PPTP is not recommended as a secure protocol for creating VPN tunnels, and users are advised to look for more secure alternatives such as WireGuard, OpenVPN, and IKEv2. These protocols offer strong encryption and security features without sacrificing performance, providing users with greater protection against cyber threats.
How does a PPTP connection compare to other protocols?
VPN protocols vary in their design and capabilities, each presenting unique advantages and disadvantages. They serve the fundamental purpose of establishing secure and encrypted connections between a user’s device and a VPN server. With distinct characteristics customized to specific scenarios, these protocols cater to diverse user preferences and requirements. Among the most prevalent VPN protocols are WireGuard, IPsec/IKEv2, OpenVPN, SSTP, PPTP, and L2TP/IPsec, each offering a spectrum of features ranging from heightened security measures to optimized connection speeds.
Understanding the intricacies of each protocol empowers users to select the most suitable option based on their individual needs. Different protocols employ varying levels of encryption and authentication mechanisms, ensuring flexibility in accommodating users’ security preferences. For an in-depth exploration of these protocols and their functionalities, a comprehensive overview is available here.
FAQ



























