When it comes to VPNs, many people think of it as some kind of obscure technology full of abbreviations that sound like something from the future. WireGuard, PPTP, IKEv2 – sounds like code from a sci-fi movie, doesn’t it? But don’t worry, I’m here to clarify things to the point where even a little kiddo will be aware of what lies behind these scary acronyms.
What are VPN Protocols?
A VPN protocol is a set of rules that specify how your online data travels from your device, through a VPN server, and then to the Internet. Without a VPN, your online data travels over the IP address, just like you might use to drive to work. However, when using a VPN, your data is rerouted through a secure, encrypted tunnel before reaching its destination. This requires a separate set of rules known as the VPN protocol, much like getting navigational instructions for an unfamiliar route. VPN protocols are important components of cybersecurity, that define how data is encrypted.
In addition to providing directions, VPN protocols also determine such factors as connection speed, security, and overall reliability. Just as different routes offer different distances and conditions, the choice of VPN protocol affects aspects such as encryption standards, routing of traffic through specific ports, and connection stability.
What the VPN Protocol is Not
VPN protocols are not a universal solution to protect against cybersecurity threats. While they play a vital role in encrypting and transmitting data between devices and servers, it is important to be aware of their limitations. Contrary to popular misconception, VPN protocols do not offer complete protection against all online security risks. They do provide a certain level of protection, but users must remain aware of their limitations and implement additional security measures to effectively minimize potential threats. This understanding is critical to making informed decisions about online privacy and security, ensuring that users take a comprehensive approach to protecting their digital identities and sensitive information.
6 The Most Common VPN Protocols
VPN protocols come in different forms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. They are used to establish secure and encrypted connections between a user’s device and a VPN server. Each protocol has different characteristics that make them suitable for different use cases. Here are some of the most common types of VPN protocols we’ll cover: WireGuard, IPsec/IKEv2, OpenVPN, SSTP, PPTP, and L2TP/IPsec. These protocols offer a range of features, from enhanced security to optimized speeds, to meet the diverse preferences and requirements of users. By understanding the nuances of each protocol, users can choose the most appropriate option for their specific needs, ensuring a balance between security, performance, and communication.
WireGuard
WireGuard is widely regarded as the future of VPNs for several good reasons. Its advanced security and easy setup make it a favorite among users. Offering flexibility and fast connection recovery, it supports the efficient User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Unlike its competitors, WireGuard features a simplified but reliable coding framework. Thanks to its use of UDP, it outperforms other protocols such as OpenVPN and IKEv2 in speed tests. Despite its impressive performance, WireGuard is still under development and may not be suitable for users who need built-in cloaking features for a stable connection, especially in regions such as China. In addition, it temporarily saves the connected IP addresses on the server until a reset.
Overall, for most users looking for high performance, ease of use, strong encryption, streaming, and gaming – WireGuard remains an excellent choice. Still, there is always room for improvement, which makes Wireguard take a close look at customer maintenance and check network performance. WireGuard’s lack of dynamic address management poses challenges for maintaining user privacy, requiring the storage of sensitive data that contradicts our strict no-logs policy.

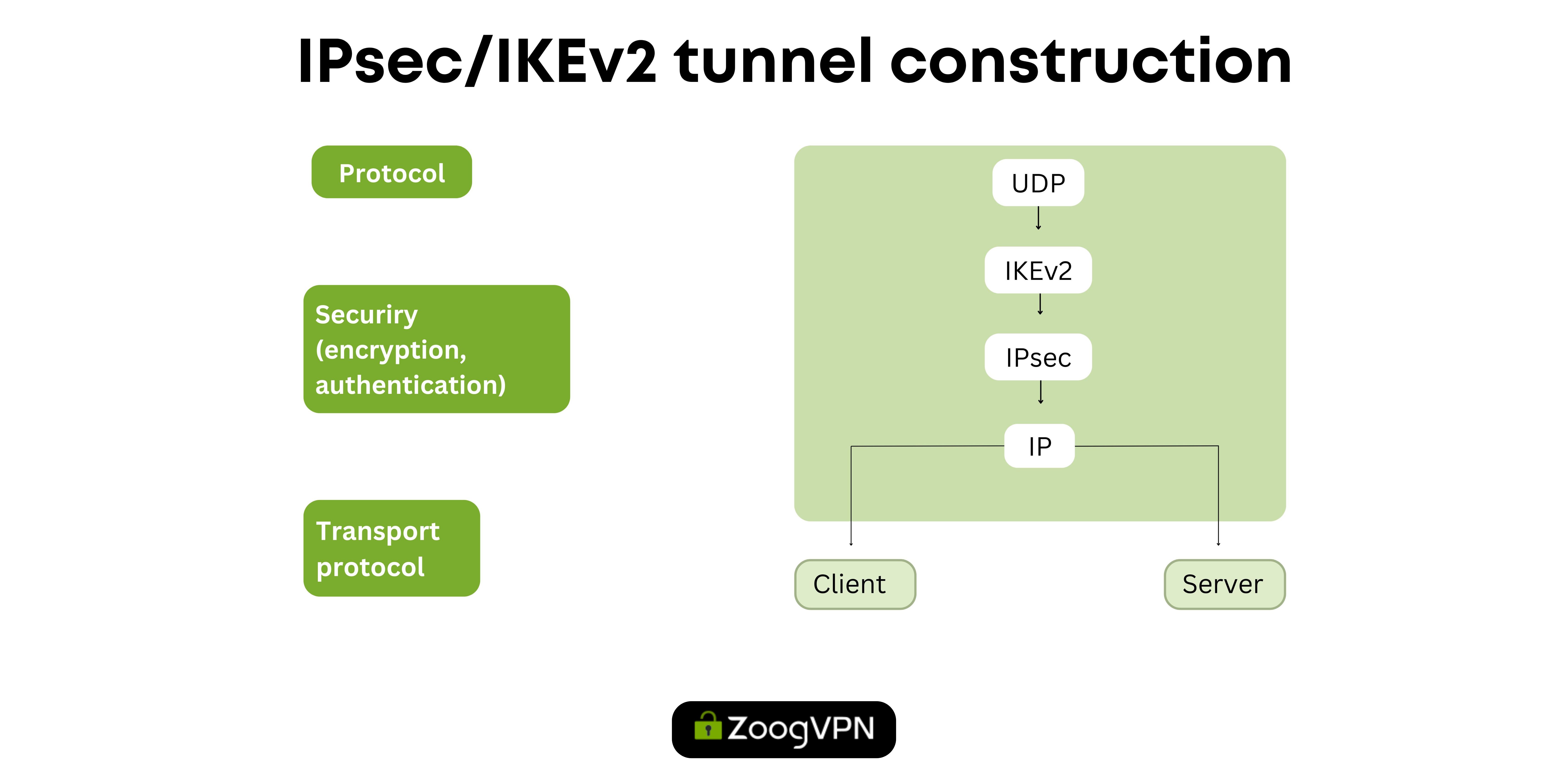
IPSec / IKEv2
IPSec / IKEv2 is a reliable VPN protocol with strong encryption known for its stability, security, and speed. With features such as Mobility Protocol and Multihoming, it provides a reliable connection even when switching between Wi-Fi and mobile data. However, its complex configuration can be challenging for newer users. IKEv2 is fast and secure, offering higher speeds, stability, and automatic connection reconnection compared to OpenVPN. The mobility and multi-hosting protocol further enhances its adaptability, making it ideal for mobile users and travelers. Despite its advantages, some firewalls may block IKEv2 due to the use of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port 500. All in all, IPSec / IKEv2 is a great choice for those who prioritize performance and security in their VPN connections.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is a renovated and widely used VPN protocol, that offers strong security and flexibility, running on either the Transmission Control (TCP) or User Datagrama (UDP) Internet Protocols to ensure data transmission integrity and speed. Its open-source code ensures transparency, allowing users to check the code for potential vulnerabilities. OpenVPN’s versatility extends to its compatibility with a variety of encryption and traffic protocols, meeting a variety of security needs. Although it easily overcomes most firewalls and provides a stable connection, its complex setup process may discourage some users from creating their own servers. Nevertheless, OpenVPN remains an excellent choice for comprehensive protection, especially on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks, and its compatibility with a variety of operating systems and devices makes it widely available.

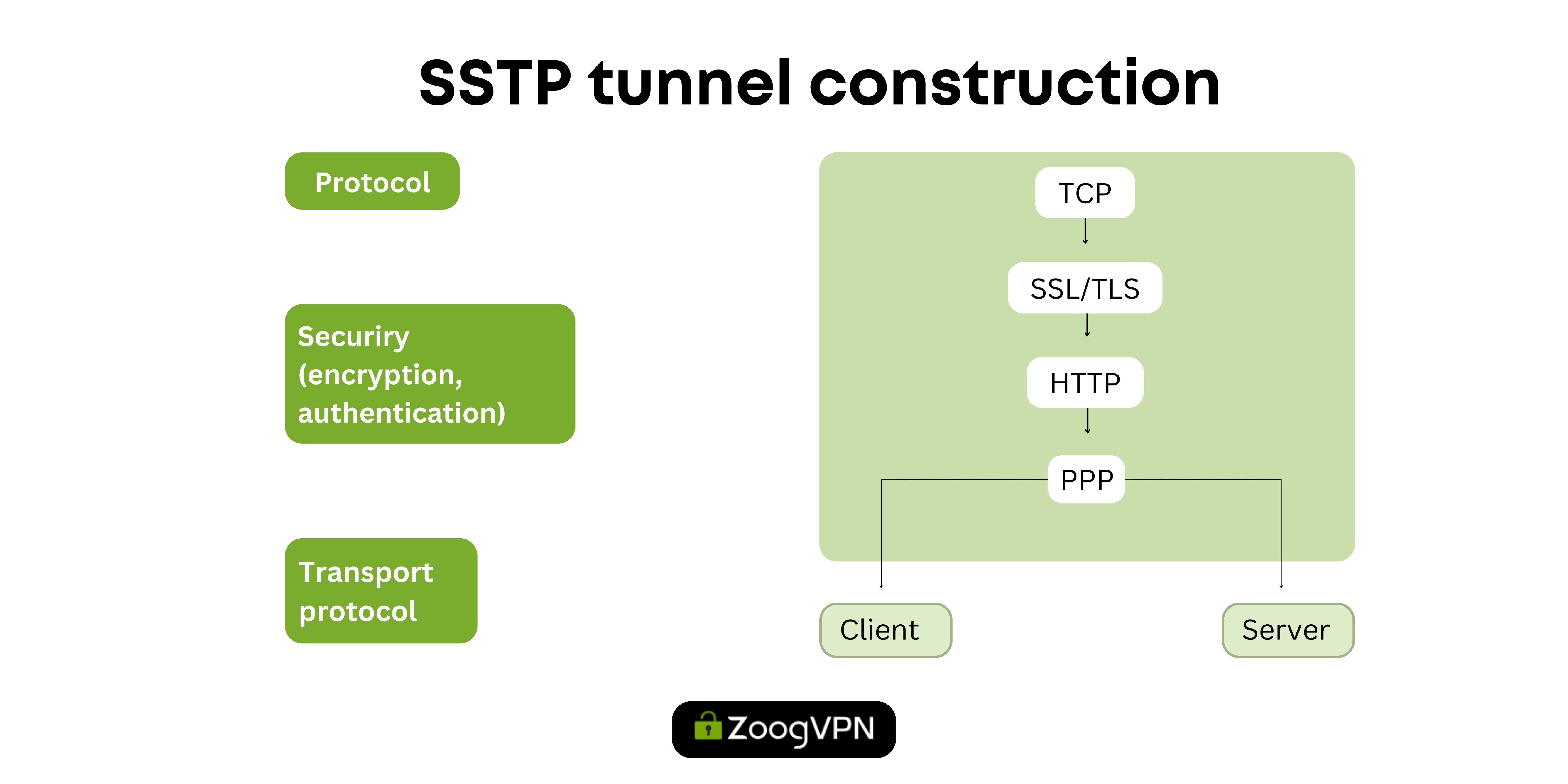
SSTP
The Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP), developed by Microsoft, is known for its compatibility with Windows, meanwhile offering a balance of security and capabilities in the VPN protocol space. Although it provides strong encryption with AES-256 like other leading protocols, its affiliation with Microsoft raises concerns about potential accountability and backdoors that are not accessible to security researchers, in addition users may experience slow flow of work using that protocol. Despite this disadvantage, SSTP does a great job of evading firewalls, providing smooth communication, and increasing privacy while surfing the web. Users should carefully weigh these factors to determine if SSTP meets their security and privacy needs, given its availability not only for Windows but also for other operating systems.
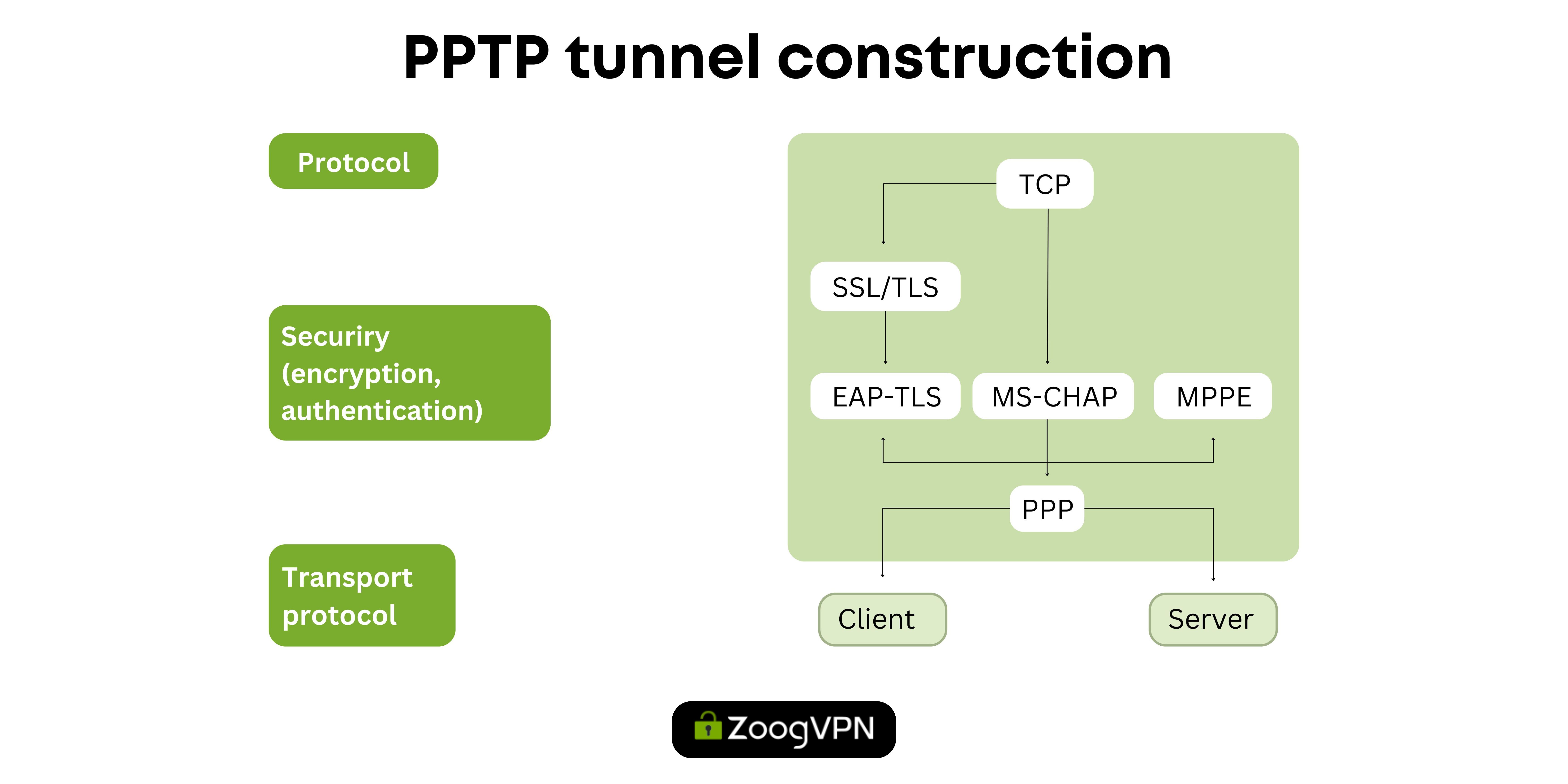
PPTP
The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), developed in 1999, was the first widely available VPN protocol, primarily used to tunnel dial-up traffic. Dial-up is a technology used to connect to the internet using a standard telephone line. It works by dialing a specific phone number provided by an internet service provider (ISP) and establishing a connection through a modem. Despite its speed and wide compatibility with a variety of systems and devices, PPTP has significant weaknesses due to weak encryption, making it sensitive to exploitation and decryption by organizations such as the National Security Agency (NSA). While its simplicity makes it easy to set up and operate, PPTP’s insecure nature and vulnerability to firewall blocking make it inappropriate for secure VPN connections, especially in environments where data privacy and security are of paramount importance. Despite its shortcomings, PPTP’s minimal overhead due to weak encryption results in average connection speeds, although at the expense of decreased security.
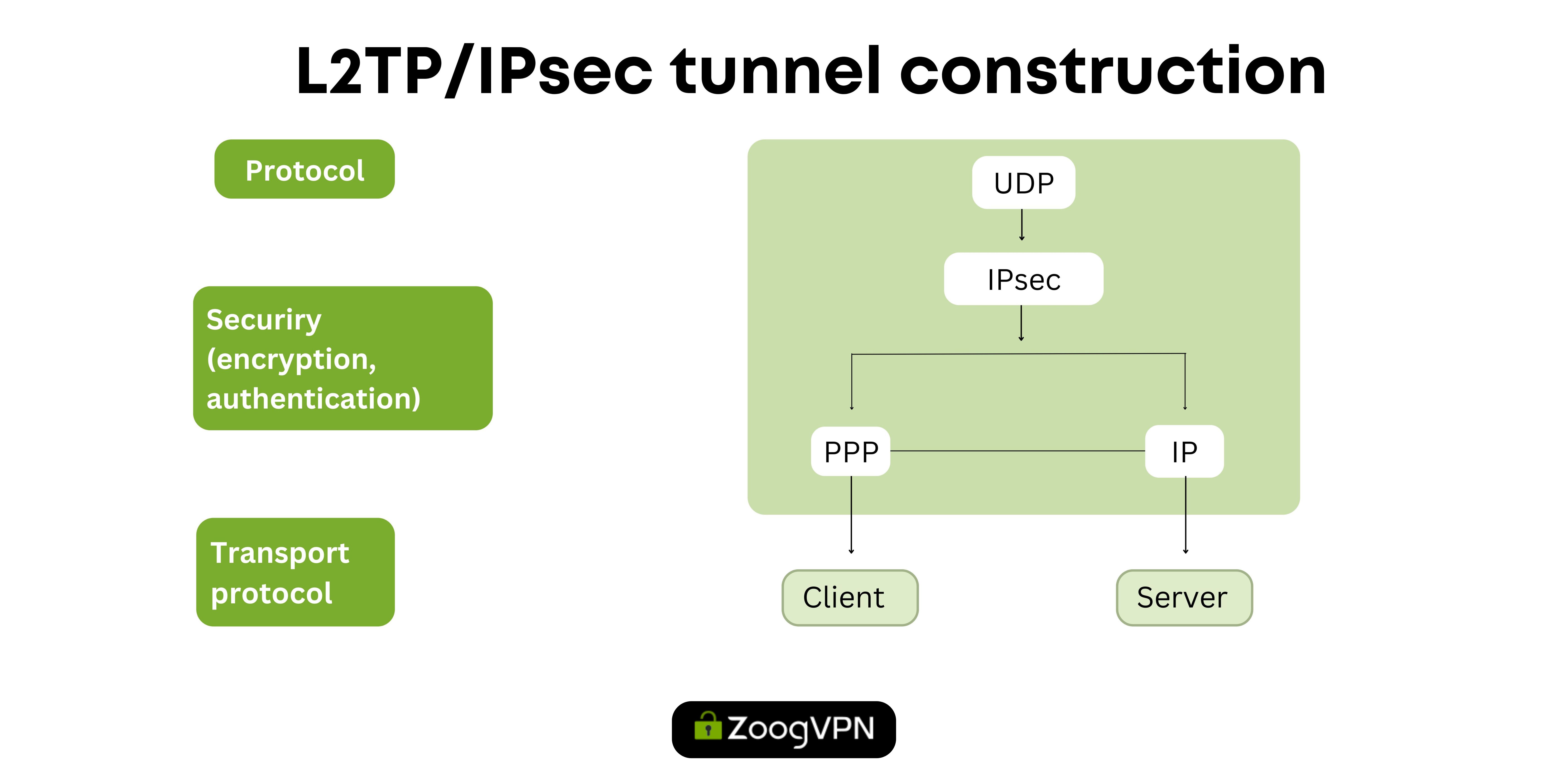
L2TP/IPSec
The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) works in tandem with Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) to create a VPN protocol known for its wide availability and robust security features. L2TP does not have encryption and authentication capabilities on its own but uses IPsec to perform these important functions, offering flexibility in security configurations. Its compatibility with various encryption protocols and wide device support make it an attractive option for administrators looking for secure VPN solutions across multiple platforms. However, the double encapsulation of L2TP/IPsec data can result in slower connection speeds than other protocols, and the lack of sophisticated firewall-overcoming features can pose problems in limited network environments. Despite these limitations, L2TP/IPsec remains a well-grounded choice, especially for organizations looking to securely connect multiple branch offices into a single network.
Each of these VPN protocols address different user needs and priorities. Some prioritize speed, which is ideal for streaming and gaming, while others prefer strong encryption for maximum privacy and security. Additionally, compatibility with devices and platforms varies by protocol, with some working better on certain devices. For example, IKEv2 works great on the IOS because of its built-in support, while Android users may have difficulty setting it up. Therefore, choosing the right protocol depends on individual needs, user cases, and device compatibility.
Full Comparison of VPN Protocols
For those seeking a comprehensive comparison of VPN protocols, the following table provides insights into their performance, security features, and compatibility:
| VPN protocol | Speed |
Encryption |
Streaming |
Stability | P2P |
Available in ZoogVPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Wireguard |
Very fast |
Very good |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Yes |
|
IPsec/IKEv2 |
Fast |
Very good |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Yes |
|
OpenVPN |
Fast |
Very good |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Yes |
|
SSTP |
Average |
Good |
Average |
Average |
Good |
No |
|
PPTP |
Fast |
Poor |
Poor |
Poor |
Poor |
Manual |
| L2TP/IPSec | Average | Average | Poor | Poor |
Poor |
Manual |
Which VPN Protocol is the Best?
Choosing the best VPN protocol depends on individual requirements and priorities, taking into account factors such as speed, security, compatibility, and specific use cases. Torrent streaming, a balance between speed and privacy is crucial, making it an appropriate choice for WireGuard, and OpenVPN. In gaming, keeping latency low is essential for a smooth experience, so fast tunneling protocols such as IKEv2, or WireGuard are preferred. For privacy-conscious users, protocols such as WireGuard, OpenVPN, and IKEv2 offer reliable security features. IOS Mobile users can benefit from the stability and fast connection recovery of IKEv2, while older devices may find compatibility with protocols such as L2TP/IPSec or PPTP. Additionally, most routers typically support older protocols such as PPTP, L2TP and IPSec, and some also support OpenVPN. However, our unique offering includes the ability to use WireGuard VPN with routers, which sets us apart from many competitors. For more information or assistance in setting up the fastest WireGuard VPN for your router, feel free to contact us.
At ZoogVPN, we prioritize user needs by offering a range of fast protocols for our applications. We’re committed to adapting to industry changes and even developing custom solutions like the Shadow and ZoogTLS protocols to navigate strict internet censorship. We aim to provide the best possible experience for all our users, ensuring speed, security, and stability in any scenario.
Fastest VPN Protocol
When it comes to speed, WireGuard and IKEv2 prove to be the fastest VPN protocols, followed by OpenVPN, PPTP, and L2TP, which also offer commendable speeds. WireGuard, in particular, stands out for its lightweight design, requiring a minimal number of lines of code to implement. This simplified design results in a reduced number of background processes, increasing overall speed and efficiency. For users who prioritize speed, WireGuard is often highlighted as the best choice because it minimizes lagging and maximizes traffic flow. Its fast and efficient operation makes it particularly suitable for data-intensive applications such as streaming and gaming.
The Most Secure VPN Protocol
When it comes to VPN protocols, security is on top, and OpenVPN and WireGuard stand out as the most secure options available. OpenVPN offers outstanding encryption capabilities, supporting the industry’s highest standard of 256-bit AES encryption and relying on the robust OpenSSL cryptographic toolkit for secure communication standards. At the same time, WireGuard utilizes state-of-the-art cryptography using ChaCha20 encryption, offering a secure alternative with less attack surface compared to OpenVPN.
However, despite its advanced security features, WireGuard is still under development. In contrast, IKEv2 and L2TP offer a sufficient level of security with support for different levels of AES encryption and use IPSec for encryption. However, after Edward Snowden’s leaks, concerns have been raised about the integrity of IPSec, which raises questions about potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by intelligence agencies.
In particular, PPTP is the least secure option, suffering from serious vulnerabilities in its authentication protocol and encryption standards. Therefore, for users who prefer privacy and security, OpenVPN and WireGuard are the best choices, offering strong encryption and advanced security features to protect sensitive data and ensure online privacy.
See about military grade VPN encryption.
Conclusion
Consequently, VPN protocols are irreplaceable tools for reinforcing online privacy and security in the face of the constant challenges facing the digital landscape. By delving into the details of different protocols and identifying their individual advantages and disadvantages, users are able to make informed decisions based on their specific priorities. Whether the focus is on speed, security, or interoperability, the variety of VPN protocols available ensures that every user can find the right solution to meet their unique needs. With the flexibility to configure protocols on the fly and the guidance provided in this detailed guide, users can confidently navigate the complexities of VPN connections. So keep this guide handy so you can set up a VPN connection at a moment’s notice and effectively protect your digital life.



























